Arrays, Loops, Imports
-
A Guide to Java Loops
Loops in Java
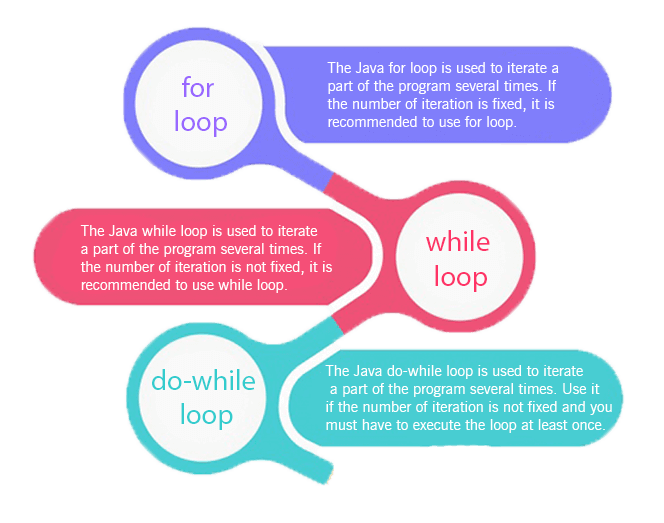
The Java for loop is used to iterate a part of the program several times. If the number of iteration is fixed, it is recommended to use for loop.
There are three types of for loops in Java.
## types of loops
* Java Simple for Loop
initialize the variable, check condition and increment/decrement value. It consists of four parts:
- Initialization: It is the initial condition which is executed once when the loop starts. Here, we can initialize the variable, or we can use an already initialized variable. It is an optional condition.
- Condition: It is the second condition which is executed each time to test the condition of the loop. It continues execution until the condition is false. It must return boolean value either true or false. It is an optional condition.
- Increment/Decrement: It increments or decrements the variable value. It is an optional condition.
- Statement: The statement of the loop is executed each time until the second condition is false.
Syntax:
for(initialization; condition; increment/decrement){
//statement or code to be executed
}
]
While loop
The Java while loop is a control flow statement that executes a part of the programs repeatedly on the basis of given boolean condition.
When use While loop
If the number of iteration is not fixed, it is recommended to use while loop.
Syntax:
while(condition){
//code to be executed
}
-
Do-While loop
The Java do while loop is a control flow statement that executes a part of the programs at least once and the further execution depends upon the given boolean condition.
When use do While loop
If the number of iteration is not fixed and you must have to execute the loop at least once, it is recommended to use the do-while loop.
Syntax:
do{
//code to be executed
}while(condition);
-
Imports
Package = directory. Java classes can be grouped together in packages.
Package declaration
The first statement, other than comments, in a Java source file, must be the package declaration.
Package declaration syntax
- Package statment (optional).
- Imports (optional).
- Class or interface definitions.
Imports: three options:
- he most common programming style:
import javax.swing.*; The wildcard character (*) is used to specify that all classes with that package are available to your program.
- Classes can be specified explicitly on import instead of using the wildcard character:
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
- Alternately we can the fully qualified class name without an import.
javax.swing.JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, "Hi");